
Rework involves restoring a product to its original specifications when it fails to meet predefined requirements during in-process inspection. Once corrected, the product fully complies with the original standards.
Depending on the workflow, rework can either be performed immediately on the production line when an operator identifies an issue, or the product can be removed from the main flow and sent to a dedicated rework station for further analysis and rectification.
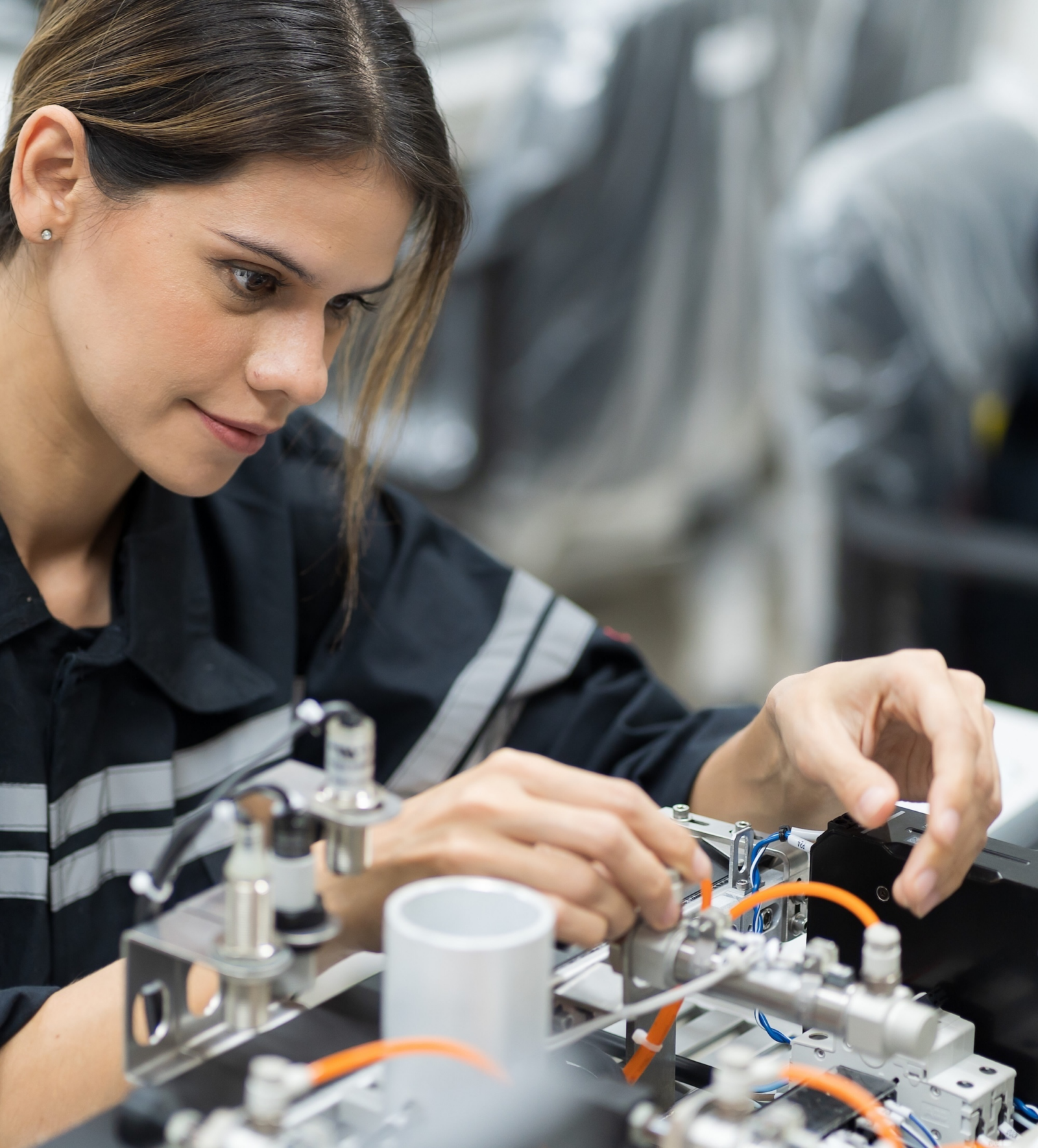


Although operator guidance primarily aims to eliminate human errors at the source, rework is sometimes necessary, either during the process itself or at a separate rework station. However, this process also comes with its own set of challenges.
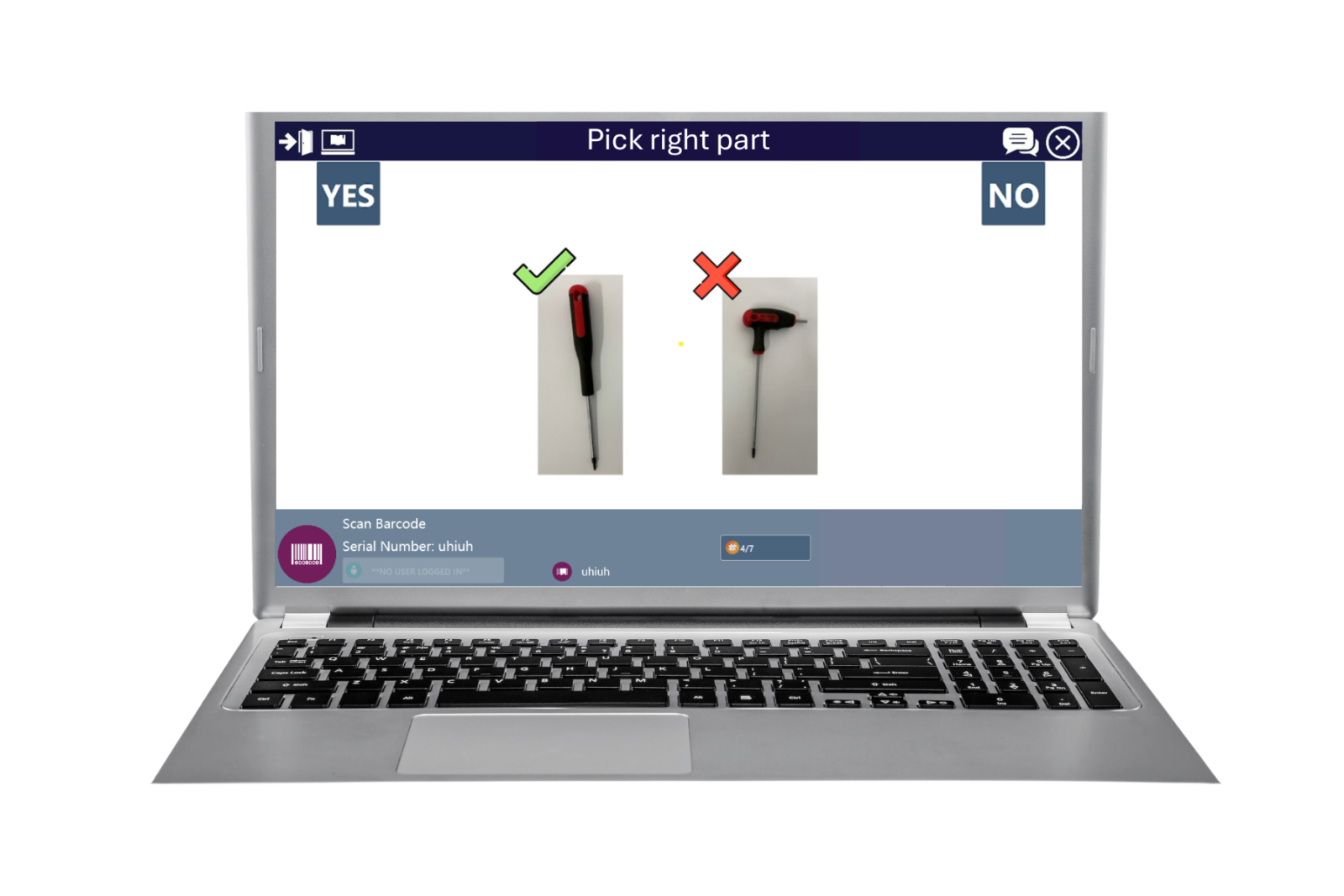
Digital work instructions (DWIs) are electronic replacements for traditional paper manuals, providing operators with step-by-step guidance for assembly, repair, or operational tasks through digital devices such as computers, tablets, or smartphones.
Advantages

Mobile work instructions give technicians clear, up-to-date guidance on portable devices like tablets, allowing them to move freely during repairs. This eliminates trips to fixed stations or paper manuals, improving efficiency and reducing errors.

Augmented Reality (AR) projected onto workstations transforms repair and rework processes by overlaying digital instructions, visuals, and guidance directly onto the physical workspace. This hands-free, context-aware approach allows technicians to see exactly where and how to perform each step, improving accuracy, speed, and safety. By eliminating the need to look away at manuals or screens, AR keeps focus on the task at hand, reducing errors and rework. The result is a more intuitive, efficient, and consistent repair process that enhances quality, accelerates training, and supports a smarter, connected production environment.

Cameras and machine vision systems are highly valuable in repair and rework operations because they provide precise, automated visual inspection that ensures defects are correctly identified and repairs meet quality standards. By capturing detailed images before, during, and after the repair, vision systems help verify correct part placement, alignment, and surface condition with consistency far beyond human inspection. They also enable real-time defect detection, documentation, and traceability, reducing the risk of incomplete or incorrect rework.
Step into the future of guided manufacturing.