Augmented Reality (AR) is becoming increasingly valuable in the automotive industry, offering significant benefits across design, manufacturing, and training. The primary goal of AR integration is to create a more intuitive and interactive experience that enhances efficiency, improves quality, and reduces training time.
By merging the physical and digital worlds, AR provides clearer, more accessible information for decision-making and navigation. Whether designers, technicians, or operators, it enables users to receive real-time guidance and visual instructions, resulting in safer and more accurate operations.
AR is especially impactful in manufacturing, where it is currently the most widely used. Here, it supports workers with step-by-step instructions, minimizes errors, and streamlines production processes. As AR technology continues to evolve, its influence in the automotive sector is expected to grow steadily, shaping a smarter and more connected future.

AR glasses and wearables offer a hands-free, mobile solution for delivering real-time support and guidance in the automotive industry. By using AR glasses, experts can remotely connect with field technicians anywhere in the world, seeing exactly what the technician sees and providing immediate advice on what actions need to be taken.
Use cases include field service, maintenance tasks, and mobile warehousing, where quick, on-the-spot support is essential. These tools allow for faster troubleshooting and reduce downtime, especially when expert personnel are not physically present.
Pros of AR glasses include their mobility and hands-free functionality, making it easier for technicians to follow instructions while keeping their hands free for the task at hand. Remote experts can assist without being on-site, improving efficiency and response times.
However, there are also limitations. AR glasses are generally not designed for prolonged use, and battery life can be an issue during long shifts. They may also obstruct the user’s field of view, which can impact safety and effectiveness on the shop floor. From practical experience, their success in day-to-day operations is often limited. While they can be valuable for initial training or specific, short-term tasks, their use in ongoing production environments remains challenging.
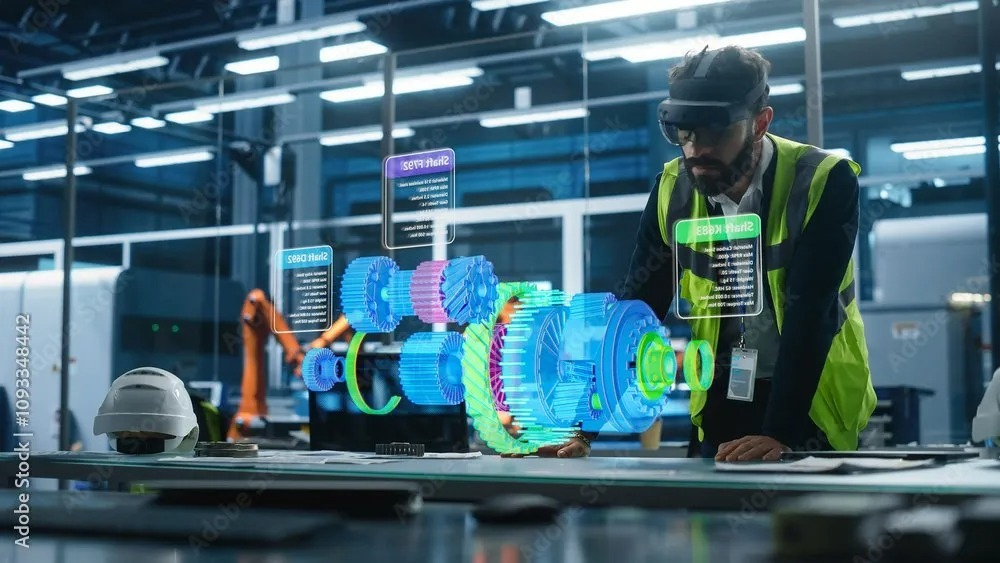

Tablets are commonly used in the automotive sector to provide on-demand instructions by simply hovering over or scanning an object to display relevant tooltips and guidance. This method offers a quick and interactive way to access information, making it useful for tasks like field training and referencing service manuals.
Use cases include technician training, maintenance guidance, and accessing digital manuals on the go. The ability to visualize components and instructions digitally enhances understanding, especially for less experienced workers.
One of the key advantages of using tablets is user familiarity, most people are already comfortable with smartphones and tablets, which reduces the learning curve.
However, there are notable challenges. Tablets are not ideal for step-by-step assembly tasks, as they require the user to operate them with at least one hand, making it difficult to work hands-on. They can also suffer from battery issues if not properly charged and require users to divide their attention between the screen and the task, which may reduce focus and accuracy. Additionally, since tablets are general-purpose devices, there is a risk of them being used for non-work-related activities, potentially impacting productivity.

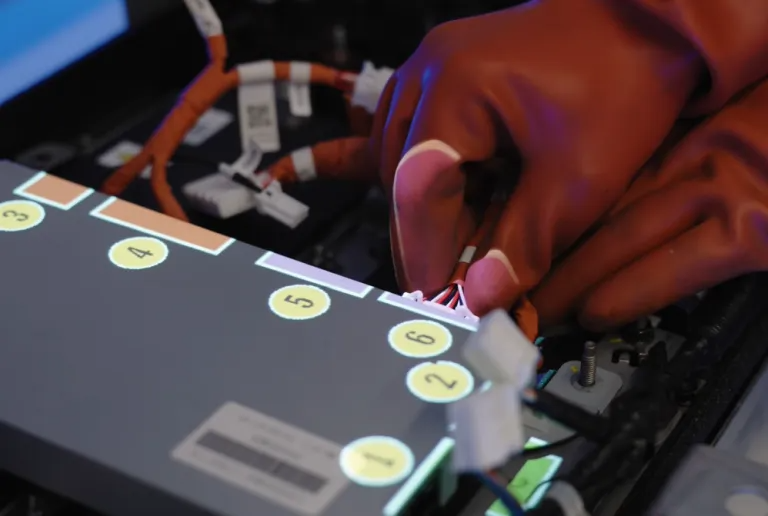
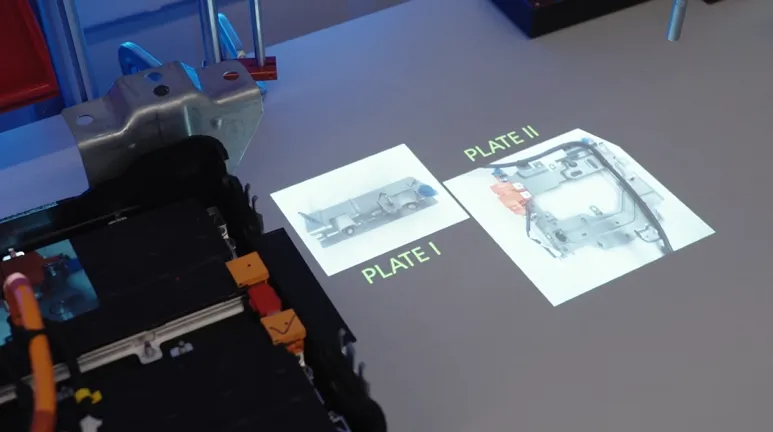
Projection-based augmented reality involves using a projector to display visual instructions, such as images, shapes, colors, text, and videos, directly onto the work area. This technology is typically brand-agnostic and can be applied to various tools or surfaces to guide operators in real time.
Use cases include standardizing work instructions, supporting complex assembly tasks, on-the-job training, part picking and kitting, and processes like tightening where precision and sequence are essential. The system delivers guidance exactly where the operator is working, enhancing clarity and reducing errors.
One of the main advantages of projection-based AR is that it provides the right information at the right time, without distracting the operator. Since the instructions appear directly in the work zone, there is no need to constantly look away at a separate screen or device. Operators can keep their hands free and remain focused, improving both efficiency and safety. Additionally, because the system is stationary and connected to a power source, it can be used continuously without concerns about battery life.
However, there are also limitations. Projection systems must be installed in a fixed location, which reduces flexibility compared to mobile solutions. In some cases, particularly among older or more experienced operators, the projections can be perceived as intrusive or unnecessary, especially if they are already familiar with the tasks. Adoption may therefore require change management and training to ensure smooth integration into existing workflows.
Among the various AR technologies used in the automotive industry, projection-based augmented reality stands out as the most widely adopted on the shop floor in automotive industry. This is largely because it is the only AR solution that is truly suited for long-term, continuous use in production environments. Unlike wearables or tablets, projection-based AR does not require operators to shift focus, wear extra equipment, or manage battery life. Instead, it delivers visual instructions directly onto the work surface, keeping the operator’s attention exactly where it needs to be.
Its non-intrusive, hands-free design supports better concentration, improved task accuracy, and enhanced safety. This makes it especially effective for applications such as assembly, training, and part picking, where clear, standardized instructions are critical.
Moreover, because projection systems are stationary and brand-agnostic, they are easy to integrate into existing workflows and can be used 24/7 without operational disruption. For these reasons, projection-based AR is not only the most practical AR solution for industrial settings, but also the most accepted particularly among experienced operators. It offers a highly effective blend of innovation and usability, making it a strong choice for scaling AR in automotive manufacturing.